MolDockLab
Finding the optimal docking pipeline for consensus structure-based virtual screening (SBVS) and the diversity nature of protein are challenging. To address this challenge, we introduce MolDockLab, a novel framework designed to identify the most convenient combination of docking tools, scoring functions, and consensus ranking methods tailored for a target of interest.
Consensus structure-based virtual screening (SBVS) has demonstrated high performance in hit identification, as shown in DockM8 [1]. By leveraging a small data set of approximately 200 molecules, MolDockLab offers a fully automated pipeline. It identifies the most efficient combination of docking tools, scoring functions, and ranking methods for consensus SBVS, which is then applied to larger datasets. The top compounds are further processed to select the most promising candidates, as illustrated in Figure 1.
Energy-coupling factor transporters (ECF-T) are novel and promising antimicrobial targets that mediate micronutrient transport into the cell [2]. As a case study, MolDockLab was deployed for ECF-T hit identification, leading to the discovery of two promising hits in in vitro assays. Testing similar compounds resulted in the identification of nine additional hits, demonstrating the efficacy of MolDockLab.
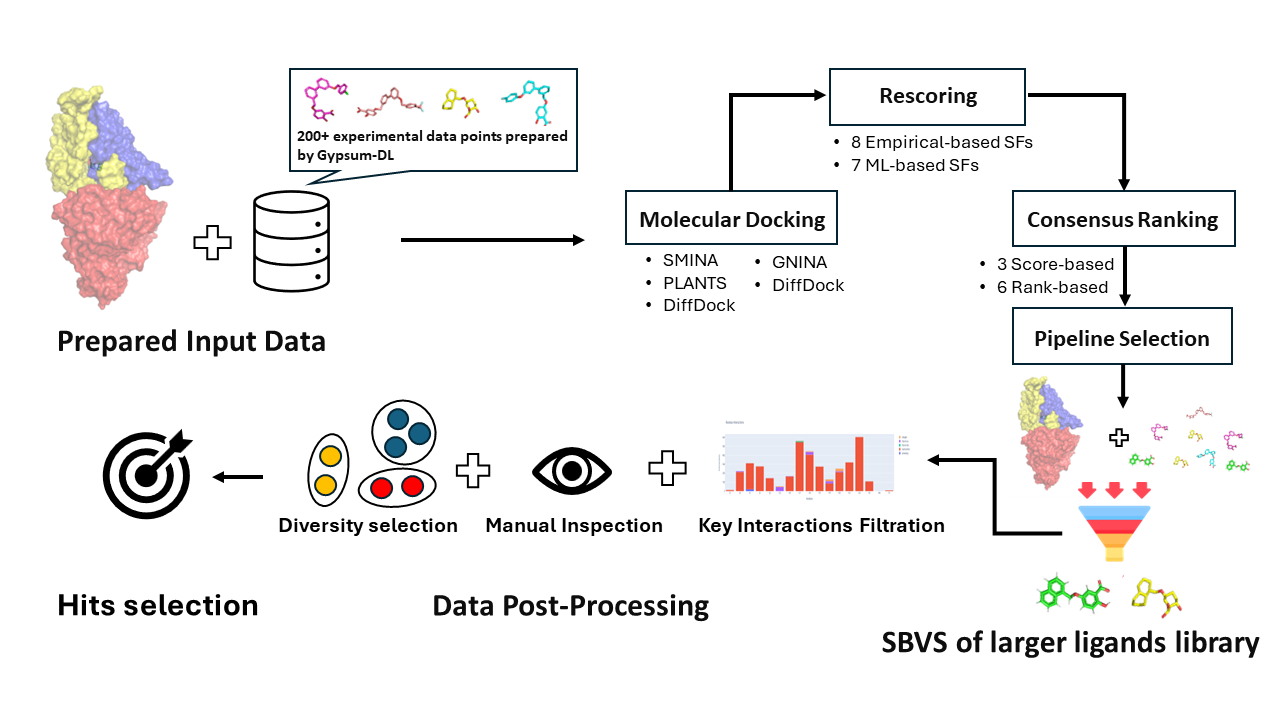
Figure 1: Overview of MolDockLab Pipeline
Software and resources
People
- Ioulia Antonia Exapicheidou · HIPS
- Mostafa Hamed · HIPS
- Anna K. H. Hirsch · HIPS